Understanding coinsurance is essential for anyone navigating health insurance in the U.S.
It directly impacts your out-of-pocket expenses and determines how much you pay versus your insurance company for medical services.
Many people confuse coinsurance with copayments or deductibles, but knowing the difference can save you hundreds or even thousands of dollars.
In this article, we’ll break down everything about coinsurance, from how it works to real-world examples, tips for managing costs, and how it interacts with HRAs, ACA Marketplace plans, and other health benefits.
What Is Coinsurance?
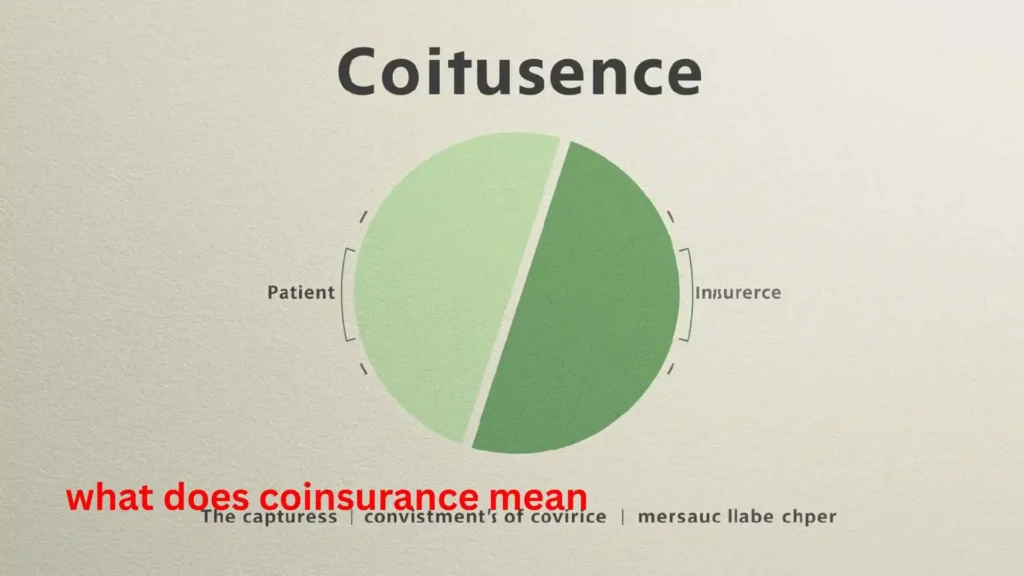
Coinsurance is the percentage of a medical bill that a policyholder must pay after meeting the deductible. For example, if your plan has an 80/20 coinsurance rate, the health insurer pays 80% of eligible costs, and you pay 20%.
It’s different from a copayment, which is a fixed fee (like $30 per doctor visit), and from a deductible, which is a set amount you must pay before insurance begins to cover costs.
“Understanding coinsurance is key because it determines your share of the costs after your deductible is met.” — Health Insurance Experts
Key points about coinsurance:
- Paid as a percentage of covered medical services.
- Only applies after deductible amounts are met.
- Contributes to your out-of-pocket maximum.
- Varies by plan type and whether you use in-network or out-of-network providers.
How Coinsurance Works
Here’s the step-by-step process to understand coinsurance:
- Meet your deductible first
- Before coinsurance applies, you must pay your full deductible.
- Example: If your deductible amount is $1,500, you pay that first.
- Before coinsurance applies, you must pay your full deductible.
- Insurance covers a percentage
- After meeting the deductible, your plan pays according to the coinsurance rate.
- Example: For a $1,000 hospital bill and 80/20 coinsurance, the insurance company pays $800, and you pay $200.
- After meeting the deductible, your plan pays according to the coinsurance rate.
- Track your costs toward the out-of-pocket maximum
- Coinsurance payments count toward your out-of-pocket maximum.
- Coinsurance payments count toward your out-of-pocket maximum.
Example Table – Coinsurance Calculation
| Bill Amount | Deductible Met | Coinsurance Rate | Your Share | Insurer Share |
| $1,000 | Yes | 80/20 | $200 | $800 |
| $500 | Yes | 70/30 | $150 | $350 |
| $2,000 | Yes | 90/10 | $200 | $1,800 |
Coinsurance vs. Other Health Insurance Costs
Understanding the difference between coinsurance, copays, and deductibles is crucial:
- Copayments (Copays): Fixed fees like $30 per physician visit.
- Deductibles: Amount you pay before insurance starts covering costs.
- Coinsurance: Percentage of costs you pay after the deductible.
- Out-of-pocket maximum: The most you pay in a year for covered medical services, including deductible, copays, and coinsurance.
Comparison Table – Coinsurance vs Copay vs Deductible
| Feature | Coinsurance | Copay | Deductible |
| Payment Type | Percentage | Fixed amount | Fixed total |
| Paid Before Coverage? | After deductible | Usually up front | Up to deductible |
| Affects Out-of-Pocket Max? | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Example | 20% of $1,000 | $30 doctor visit | $1,500 yearly |
In-Network vs. Out-of-Network Coinsurance
In-network providers are contracted with your health insurer and have negotiated rates. Out-of-network providers often result in higher coinsurance cost-sharing because the allowed amount is different.
Tips to save money:
- Always check if your physician, hospital, or pharmacy is in-network.
- Compare plan percentages for insurer vs. policyholder before scheduling services.
- Use the Explanation of Benefits (EOB) to track costs and see how coinsurance applies.
Example Table – Cost Difference In-Network vs Out-of-Network
| Service Cost | In-Network Coinsurance (20%) | Out-of-Network Coinsurance (40%) |
| $1,000 | $200 | $400 |
| $500 | $100 | $200 |
| $2,000 | $400 | $800 |
Coinsurance in Different Health Plans
Coinsurance rates vary depending on the type of health plan:
- Employer-sponsored group plan: Often 80/20 or 70/30.
- Individual health plan: Can vary more widely; typically 70/30 or 90/10.
- ACA Marketplace plans: Metallic tiers affect coinsurance:
- Bronze: Lower premiums, higher coinsurance.
- Silver: Moderate premiums and coinsurance.
- Gold: Higher premiums, lower coinsurance.
- Platinum: Highest premiums, lowest coinsurance.
- Bronze: Lower premiums, higher coinsurance.
- Low-deductible health plan (LDHP): Lower coinsurance but higher premiums.
- High-deductible health plans (HDHP): Higher coinsurance percentages, often paired with tax-advantaged HSAs.
Table – Coinsurance by Plan Type
| Plan Type | Coinsurance Rate | Typical Deductible | Premium Trend |
| Bronze (ACA) | 30%-40% | High | Low |
| Silver (ACA) | 20%-30% | Medium | Medium |
| Gold (ACA) | 10%-20% | Low | High |
| Platinum (ACA) | 10% | Very Low | Highest |
| Employer-sponsored LDHP | 10%-20% | Low | Medium-High |
| High Deductible Health Plan | 20%-40% | High | Low |
Coinsurance and Health Reimbursement Arrangements (HRA)

HRAs can significantly reduce your coinsurance costs.
Types of HRAs:
- Stand-alone HRA: Employer funds a fixed amount for IRS-eligible medical expenses, including coinsurance.
- Qualified Small Employer HRA (QSEHRA): Tax-free reimbursement for individual health plan premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Individual Coverage HRA (ICHRA): Covers premium reimbursement and coinsurance for personalized allowance.
- Integrated HRA / Group coverage HRA (GCHRA): Linked to employer-sponsored group plans, offsets coinsurance and deductibles.
“Using an HRA can turn a high coinsurance rate into manageable out-of-pocket costs for employees and families.”
Calculating Coinsurance
To calculate your coinsurance:
Step 1: Meet your deductible
Step 2: Apply the coinsurance rate
Formula:
Coinsurance Payment=(Allowed Amount−Deductible)×Coinsurance Rate\text{Coinsurance Payment} = (\text{Allowed Amount} – \text{Deductible}) \times \text{Coinsurance Rate}Coinsurance Payment=(Allowed Amount−Deductible)×Coinsurance Rate
Example:
- Allowed Amount: $1,200
- Deductible Met: Yes ($1,500 deductible already met)
- Coinsurance Rate: 20%
- Coinsurance Payment = $1,200 × 0.20 = $240
Tips to track coinsurance:
- Review EOBs regularly.
- Keep a spreadsheet of medical claim summaries.
- Track cumulative spending to know when you meet your out-of-pocket maximum.
Coinsurance and Preventive Care
Under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), many preventive services are fully covered without coinsurance, even if the deductible isn’t met.
Examples of preventive services:
- Annual physical exams
- Vaccinations
- Screenings like mammograms or colonoscopies
Important:
- Only applies in-network.
- Helps avoid unnecessary coinsurance charges.
Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Small Medical Procedure (In-Network)
- Bill: $500
- Deductible already met
- Coinsurance: 20%
- You pay $100, insurer pays $400
Scenario 2: Major Hospitalization (Out-of-Network)
- Bill: $10,000
- Coinsurance: 40%
- You pay $4,000, insurer pays $6,000
- Using in-network providers could save thousands
Scenario 3: Using HRA to Offset Coinsurance
- Bill: $1,500
- Coinsurance: 20% = $300
- HRA reimburses $250
- You pay only $50 out-of-pocket
Visual Table – Coinsurance Payment Scenarios
| Scenario | Bill Amount | Coinsurance Rate | HRA Coverage | Your Payment |
| Small Procedure (In-Network) | $500 | 20% | $0 | $100 |
| Major Hospitalization | $10,000 | 40% | $0 | $4,000 |
| Using HRA | $1,500 | 20% | $250 | $50 |
Tips to Manage Coinsurance Costs
- Choose the right plan: Consider coinsurance rates, deductible amounts, and metallic tiers.
- Stay in-network: Always check your allowed amount and negotiated rate.
- Use HRAs: Maximize tax-free reimbursement for coinsurance.
- Track expenses: Use medical claim summaries to see progress toward out-of-pocket maximum.
- Consider preventive care: Reduces unnecessary coinsurance payments.
“Smart use of HRAs, preventive care, and careful plan selection can cut your coinsurance costs significantly.”
Conclusion
Coinsurance is a key part of cost-sharing in health insurance. It determines how much policyholders pay versus their insurance company for medical services. By understanding deductibles, copays, out-of-pocket maximums, and using tools like HRAs, you can manage expenses effectively.

Julian West is a writer who believes that the right words can mend what life tries to break. A quiet observer of human nature, Julian finds his inspiration in fleeting moments — a whispered goodbye, an unfinished letter, a glance that says everything. Through his work, he captures these subtle emotions and transforms them into timeless quotes that stay with the reader long after the screen fades.
Julian writes not just to express, but to connect — with the lonely soul scrolling at midnight, the dreamer chasing light in darkness, and the fighter learning to breathe again. His quotes echo themes of healing, heartbreak, personal growth, and quiet strength. With a style that’s both poetic and piercing, Julian’s words are often described as “gentle punches to the heart.”
He spends his days exploring old books, journaling in cafes, and finding meaning in the small things — a sunrise, a tear, a laugh that escapes unexpectedly. Julian believes that even the softest words can start a revolution within.
📚 Published Works by Julian West
-
“Ashes & Echoes”
A hauntingly beautiful collection of quotes about loss, healing, and rising from emotional ruins. -
“Beneath the Stillness”
Quotes and reflections on inner peace, overthinking, and the battles no one sees. -
“The Ink Left Behind”
A poetic tribute to broken hearts, quiet strength, and the stories we carry but never tell.