Mathematics has many constants, but few are as essential and fascinating as e. Often appearing in calculus, exponential functions, scientific notation, and even calculators, e is everywhere, yet many people struggle to understand what it truly represents.
In this guide, we’ll answer the question: what does e mean in math. You’ll learn about Euler’s number, how it works in equations, logarithms, and scientific notation, and how to use it confidently in real-life problems.
The Basic Meaning of e in Mathematics
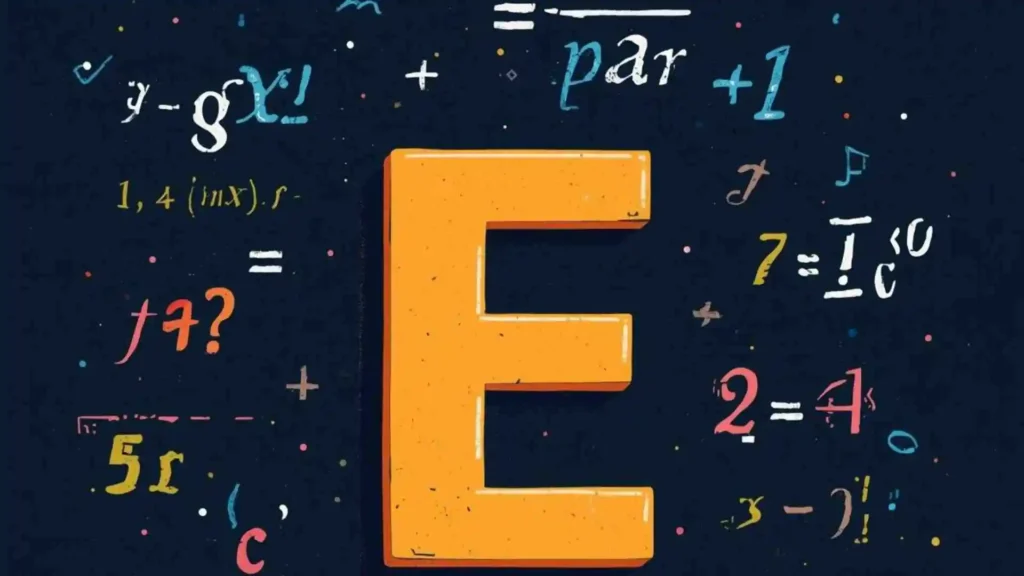
At its core, e is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 2.71828. It’s also called Euler’s number, named after the 18th-century Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, who first explored its properties.
Why e Matters
- Base of natural logarithms: ln(x) uses e as its base.
- Exponential growth and decay: Many formulas for population, interest, and radioactive decay rely on e.
- Limit definition: e = lim (n→∞) (1 + 1/n)^n, showing its connection to compounding.
Fun Fact: e is irrational, meaning it cannot be expressed as a fraction, and transcendental, meaning it’s not a solution to any algebraic equation with rational coefficients.
What Does e Mean in Math Equations
Euler’s number frequently appears in equations, especially exponential functions and differential equations. Here’s why it’s crucial:
Exponential Growth and Decay
The general formula:
[
N = N_0 e^{kt}
]
- N₀ = initial value
- k = growth (or decay) rate
- t = time
Example: If a population of 100 bacteria doubles every hour, the population after 3 hours is:
[
N = 100 \times e^{(ln(2) \cdot 3)} ≈ 800
]
Compound Interest
The formula for continuously compounded interest is:
[
A = P e^{rt}
]
- P = principal
- r = annual interest rate
- t = time in years
Example: Investing $1,000 at 5% annual interest for 3 years yields:
[
A = 1000 \times e^{0.05 \times 3} ≈ 1161.83
]
Differential Equations
Many natural systems, like radioactive decay or heat transfer, follow:
[
\frac{dy}{dx} = ky
]
Its solution is y = Ce^(kx), showing e’s natural role in change processes.
What Does e Mean in Math Logarithms

Logarithms help us invert exponentials, and e is the base of natural logarithms (ln).
- ln(e) = 1, because e^1 = e
- ln(1) = 0, since e^0 = 1
- Exponential and logarithmic functions are inverse operations
Applications
- Finance: Continuous compounding and interest calculations
- Engineering: Electrical circuits and signal decay
- Probability: Distribution of natural events
Tip: Never confuse ln(x) (base e) with log(x) (base 10). They behave similarly but use different bases.
What Does e Mean in Math Scientific Notation
On calculators, scientific notation often uses e. But here, e is not Euler’s number; it’s shorthand for “×10^”.
Example:
- 1.5e6 = 1.5 × 10⁶ = 1,500,000
- 3.2e-4 = 3.2 × 10⁻⁴ = 0.00032
This use is common in physics, chemistry, and astronomy, where very large or very small numbers appear regularly.
What Does e Mean in Math for Big Numbers
Mathematicians and scientists often deal with astronomically large numbers, like populations, distances in space, or molecular counts. Using e in scientific notation simplifies calculations and reduces errors.
Example Table: Big Numbers in e Notation
| Number | e Notation |
| 1,000,000 | 1e6 |
| 0.000001 | 1e-6 |
| Avogadro’s number (≈6.022×10²³) | 6.022e23 |
What Does e Mean in Math Sets
Occasionally, e appears in set theory or identity notation, but this is separate from Euler’s number.
- In some textbooks, e ∈ A indicates e belongs to set A
- Can also represent the identity element in algebraic structures
This usage is context-dependent and usually appears in advanced math or abstract algebra.
What Does e Mean in Math Calculators

Most scientific calculators have a dedicated e button. Here’s what it does:
- Computes e^x directly, saving time and reducing errors
- Works for exponential growth, decay, and logarithmic calculations
- Graphing calculators allow plotting y = e^x functions visually
Example: Entering e^2 gives ≈ 7.389, useful in modeling real-life scenarios.
Common Misconceptions About e in Mathematics
Many students confuse Euler’s number with:
- Approximation: e ≈ 2.71828, not exactly 2.7
- Exponential functions: e^x is a function, e is a constant
- Scientific notation: e in notation (1e6) is not Euler’s number
Understanding the distinction prevents mistakes in homework, exams, and scientific calculations.
Quick Reference Table: e Meaning by Context

| Context | Meaning / Usage |
| Basic constant | Euler’s number ≈ 2.71828 |
| Equations | Exponential growth, decay, differential equations |
| Logarithms | Base of natural logarithms (ln) |
| Scientific notation | Represents large/small numbers (1.5e6 = 1.5 × 10⁶) |
| Calculators | e^x computation button |
| Big numbers / computation | Efficient representation of exponential values |
| Sets | Rarely, membership or identity symbol |
FAQs
Why is e important in calculus?
- e allows easy differentiation and integration of exponential functions, making calculus simpler and more natural.
Is “e” irrational or rational?
- e is irrational and transcendental, meaning it can’t be expressed as a fraction or root of a rational equation.
How is e used in compound interest?
- It allows for continuous compounding, giving the most accurate calculation for growth over time.
What is the difference between e and ln?
- e is a constant, ln(x) is a function using e as the base of logarithms. They are mathematically inverse.
How do I enter e in a calculator?
- Most scientific calculators have an e button, which computes e^x directly.
Conclusion
Euler’s number e is more than just a number. It underpins exponential growth, decay, logarithms, scientific notation, and natural processes.
By mastering e, you can:
- Solve real-world exponential problems efficiently
- Use calculators and scientific notation correctly
- Understand natural logarithms and differential equations
- Apply math confidently in finance, engineering, and science
Remember: context matters. If in equations, scientific notation, or sets, e is one of math’s most powerful constants.
Also Check These Posts
- What Does PRN Mean | Slang Medical and Texting Meanings Explained for 2026
- What Does STG Mean | Full Meaning Uses Examples and How to Reply for 2026

Ethan Cole is a writer fueled by emotions, driven by truth, and inspired by the power of words. Known for his ability to distill complex feelings into short, striking lines, Ethan has become a go-to name for readers seeking comfort, motivation, and clarity through quotes.
With a background in literature and a lifelong love for poetic expression, Ethan blends simplicity with depth. He writes not just to be read, but to be felt. His work dives into themes of heartbreak, healing, mental strength, and the beauty of being human — making his words resonate across generations.
Ethan believes that even a single sentence, when written with honesty, can become a turning point in someone’s life. Whether it’s a quote to mend a shattered heart or one to spark a dream, he crafts each line with intention.
Outside the world of writing, he enjoys black coffee, rainy evenings, and observing life in its rawest form — because that’s where the real stories hide.
📚 Published Works by Ethan Cole
“Fragments of a Shattered Sun”A poetic journey through heartbreak, loss, and the light that follows even the darkest nights.
“Ink & Resilience”A bold mix of motivational quotes and raw reflections on self-growth, courage, and rising again.
“The Weight of Quiet Things”A deeply personal collection of short quotes and musings for those who feel deeply but speak softly.

